How do I know if I have an internal ear injury?


An internal injury to the ear can go unnoticed if we do not know its symptoms well, since sometimes they could be confused with other pathologies. Therefore, from Claso we want to explain to you how to recognize an internal injury in the ear.
Internal ear injuries can produce a wide variety of symptoms. For example, dizziness or vertigo, which could be confused with other conditions of the body. For this reason, it is important to know what symptoms can be caused by an internal ear injury and thus recognize it early.
Symptoms of Internal Ear Injuries
The most common symptoms that can warn you of a possible internal ear injury are:
- Intermittent beeps or tinnitus, characterized by having an internal origin that only the person suffering from it can hear.
- Dizziness or vertigo, since it is the inner ear that controls our balance.
- Discharge in the form of clear fluid, pus, or blood. In many cases it may simply be the wax that keeps the ear clean. However, it could be indicating a ruptured eardrum or an infection.
- Sudden hearing loss. Gradual hearing loss is not usually associated with an internal ear injury. Instead, we should be concerned if it is a sudden loss, since it may be warning us of an internal injury.
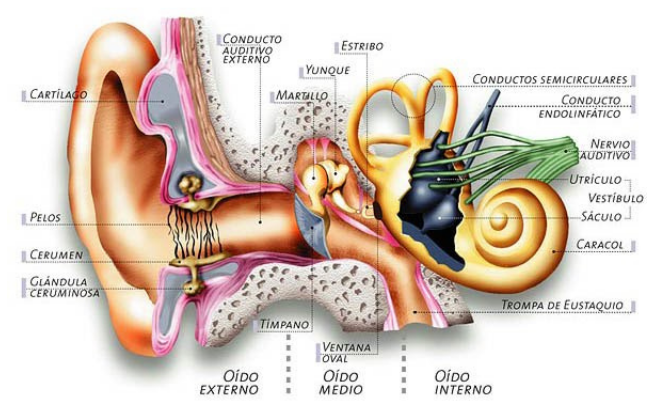
Types of Inner Ear Injury
There are different types of injury to the inner ear that can affect our hearing health. We detail the most notable ones below:
- Ménière's syndrome or disease, a disorder in the inner ear, of unknown causes, which causes dizziness, wheezing, vertigo and hearing loss.
- Vestibular neuronitis, an inflammation of the vestibular nerve that causes severe episodes of vertigo, since it is the nerve, located in the skull, that controls balance. Unlike the previous pathology, this one does not present hearing loss or whistling.
- Tubaritis or inflammation of the Eustachian tube responsible for relieving pressure in the ear.
- Perforation of the eardrum, a more common injury than it may seem. It usually occurs after a sudden change in pressure or the impact of an object, such as the ear bud, and is usually detected by the discharge of clear fluid or blood. It can also be caused by a continuous series of ear infections that end up damaging the eardrum.
From Claso we recommend that when you perceive any of the symptoms detailed above, you urgently go to the ENT. As we have already commented in previous blogs, it will be the ENT who is in charge of prescribing a pharmacological treatment for an internal ear injury. Audiologists will evaluate and solve, if necessary, the possible consequent hearing loss.