What is the eustachian tube?

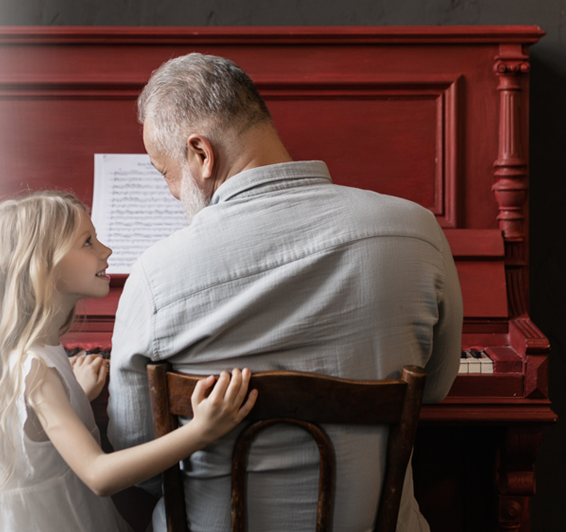
Did you know that when Beethoven premiered his Ninth Symphony he was already totally deaf? In fact, he had to turn around to see how the audience applauded and discover that the concert had been a success because he was unable to hear the ovation. We could invite you to listen to this immortal score while we tell you that, to this day, researchers have not agreed with the origin of the evil of one of the best musicians in history. However, in Genius and Drama: Beethoven's Deafness, reads as follows:
The external auditory canal, especially at the level of the eardrum, was thickened and covered with shiny scales. The Eustachian tube was very thick, presenting an oedematous mucosa and a little retracted at the level of the bone portion. In front of its orifice, in the direction of the tonsils, the presence of small scar depressions is noticeable. The nerves of the face were of considerable thickness. The auditory nerves, on the other hand, were thinned and devoid of the medullary substance...
The Eustachian tube is a part of the auditory system. Its function not only allows you to hear clearly, it also protects the inner ear from injury. It is closely linked to the respiratory system. We explain what it is and what its function is.
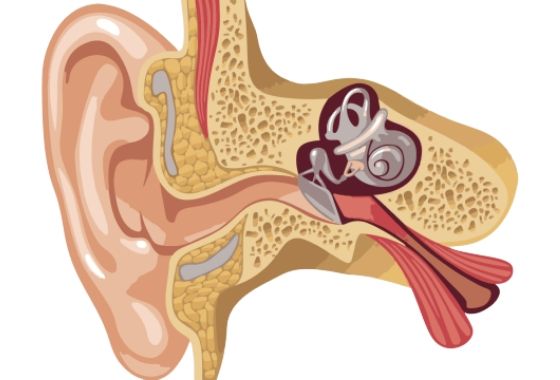
The Eustachian tube is a fundamental piece within the gear of the ear. This is because this small tube connects the throat to the middle ear. When sneezing, swallowing or yawning, the Eustachian tube opens and prevents air and fluid pressure from building up inside the ear.
It is also called the tuba or auditory tube. In any case, its main objective is to balance the middle ear pressures so that the eardrum can effectively transmit sound waves to the acoustic nerve. In addition, it protects your structures against any changes.
What is the Eustachian tube?
The name Eustachian tube comes from its shape. It is a tubular extension of between 3.5 and 5 cm similar to a horn. The tube runs from the middle ear to the nasopharynx, where it connects to the respiratory system.
In order to maintain hydration and protect itself from harmful agents, the tube has the inner walls of a mucosa covered. It is very important to maintain this hydration as it must be flexible at all times, opens and closes many times throughout the day.
How does the Eustachian tube work?
The Eustachian tube has an opening and closing system to fulfill a double function. On the one hand, it protects against the ingress of liquids and on the other it eliminates the excess pressure produced by the air or by a fluid.
All this happens so that the middle ear is always protected and works well. If the air inside is not well compensated, the sounds will not be heard clearly. The same happens if there is fluid inside the ear, the bones will not move and there will be no vibrations. When the Eustachian tube does not evacuate the pressure, there is a danger for the eardrum and a loss of hearing.
If the person feels pressure inside the ear, sometimes with pain, and the sounds are muffled, it is possible that this typical injury has occurred. Other symptoms include:
- Experiencing a clicking sensation.
- Ringing in the ears.
- In the most extreme cases, you may have trouble keeping your balance.
What is behind this Eustachian tube dysfunction?
The most common cause is when the tube becomes inflamed and fluid accumulates. It is almost always due to a cold, flu, sinusitis or various allergies. Children have shorter and narrower tubes than adults so fluid can be trapped more easily. In addition, we must not forget that their immune system is not fully developed. Smokers are another risk group because tobacco damages the cilia (the small hairs that carry mucus from the middle ear to the back of the nose). This makes it easier for mucus to accumulate in the tubes.
Sometimes the ears become clogged when yawning or blowing through the nose. This happens because air is forced into the tubes and the pressure in the inner ear increases. When you have a cold, the mucus also clogs the duct, causing hearing loss and pain in some cases.
You may be interested to know that symptoms usually go away without treatment in most cases. In fact, exercises to open the ducts, yawning or chewing gum, relieve the feeling of pressure in the ear. In the case of the baby, the soother is an excellent remedy because it stimulates the swallowing reflex.
It is very important that the Eustachian tube works correctly for the use of hearing aids. If you suffer from dizziness, if you feel constant pressure in your ear or if you suffer from excess mucus, it is necessary to consult a specialist. If you are going to choose hearing aids, it is important to know if you suffer from this dysfunction very often, so that you can find the most suitable ones within our wide and varied selection.
You know that we do not do it with any intention of generating alarm or anything remotely similar, but with the intention that you are as informed as possible in order to identify these situations, and know how to give the best possible solution.
At Claso we can help you. . Come to one of our centres and we will find a solution to improve your hearing.